Biology and Geology.Teoría,
actividades y prácticas de laboratorio. 1º ESO Programa SELE • María
del Mar Vera Sánchez
Contents and activities
UNIT 2. The Earth in the universe
2.3. THE EARTH
 YouTube: POpenMind “Why is there life on Earth?”
YouTube: POpenMind “Why is there life on Earth?”
 YouTube: CNN “NASA discovers Earth-like planet in habitable zone”
YouTube: CNN “NASA discovers Earth-like planet in habitable zone”
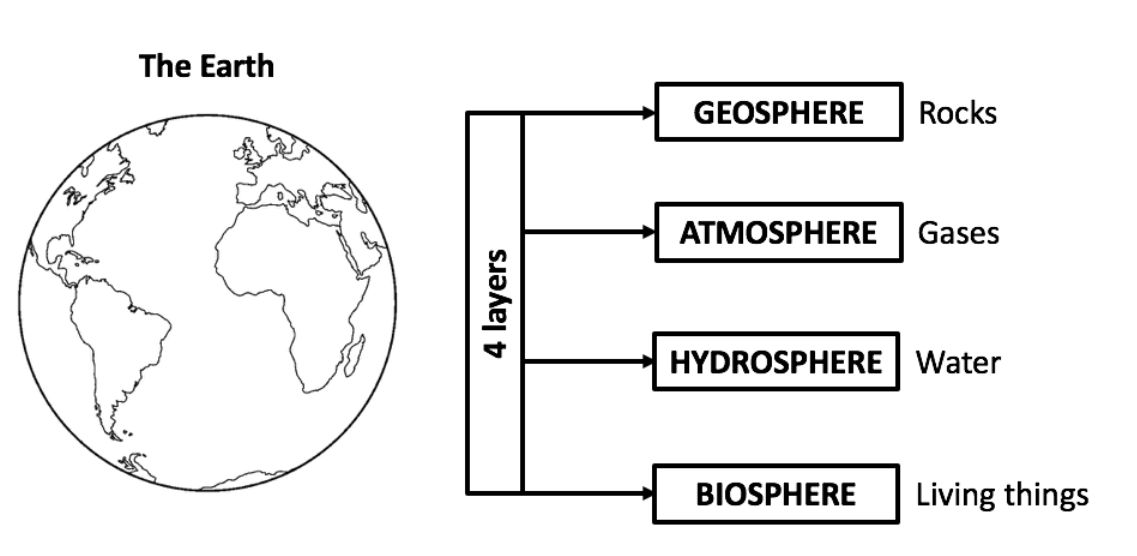
 YouTube: Happy Learning English “The Earth and its layers | Educational Video for Kids” (till 1’)
YouTube: Happy Learning English “The Earth and its layers | Educational Video for Kids” (till 1’)
-SPECIAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE EARTH
The Earth is the 3rd planet closest to the Sun. The Earth has different characteristics that make it a unique planet. The following characteristics together don’t exist in the other planets. These characteristics are:
-
TEMPERATURE
Due to its distance from the Sun, its average surface temperature is about 15 ºC. The temperatures around it make it possible for water to exist as ice, liquid and water vapor. These changes of state result in the water cycle. -
ATMOSPHERE
It contains very important gases for living things: oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are essential gases of respiration and photosynthesis. -
MAGNETIC FIELD
It protects living things from solar radiation. -
SATELLITE
The Moon causes ocean tides. -
GEOLOGICAL ACTIVITY
Erosion, volcanoes or earthquakes.
- MOVEMENTS OF THE EARTH
 YouTube: European Space Agency, ESA "Paxi - Day, night, and the seasons"
YouTube: European Space Agency, ESA "Paxi - Day, night, and the seasons"
The Earth moves into two different ways:
- ROTATION on its axis:
- It takes 24 hours (1 day) to complete one rotation.
- The consequence of rotation is the cycle of the day (sunlight) and the night (darkness).
- The tilt of the axis varies throughout the year, so the length of the day and the night also varies.
- REVOLUTION around the Sun:
- It takes 365 days (1 year) to complete one revolution.
- The distance between the Earth and the Sun is almost the same.
- The orbit of the Earth is an ellipse (almost a circle) and it is contained within the ecliptic plane.
- The consequence of the revolution and the tilt of the
axis of rotation is the annual cycle of seasons (spring, summer,
autumn and winter). There is a different amount of sunlight in
every season. According to the length of days and nights, there
are:
- Equinoxes (September equinox and March equinox): when the day and night are equal length (12 hours).
- Solstices (December solstice and June solstice): when the difference in length between day and night is the greatest.
